- Date:
- December 11, 2015
- Source:
- American Museum of Natural History
- Summary:
- The evolution of modern birds was greatly shaped by the history of our planet's geography and climate. New research finds that birds arose in what is now South America around 90 million years ago, and radiated extensively around the time of the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction. The new research suggests that birds in South America survived this event and then moved around the world via multiple land bridges while diversifying during periods of global cooling.

Modern day great blue herons.
Birds arose in what is now South America around 90 million years ago,
and radiated extensively around the time of the Cretaceous-Paleogene
extinction event that killed off the non-avian dinosaurs, according to
new research.
Credit: © SunnyS / Fotolia
New research led by the American Museum
of Natural History reveals that the evolution of modern birds was
greatly shaped by the history of our planet's geography and climate. The
DNA-based work, published today in the journal Science Advances,
finds that birds arose in what is now South America around 90 million
years ago, and radiated extensively around the time of the
Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event that killed off the non-avian
dinosaurs. The new research suggests that birds in South America
survived this event and then started moving to other parts of the world
via multiple land bridges while diversifying during periods of global
cooling.
"Modern birds are the most diverse group of terrestrial vertebrates
in terms of species richness and global distribution, but we still don't
fully understand their large-scale evolutionary history," said Joel
Cracraft, a curator in the Museum's Department of Ornithology and
co-author of the paper. "It's a difficult problem to solve because we
have very large gaps in the fossil record. This is the first
quantitative analysis estimating where birds might have arisen, based on
the best phylogenetic hypothesis that we have today."
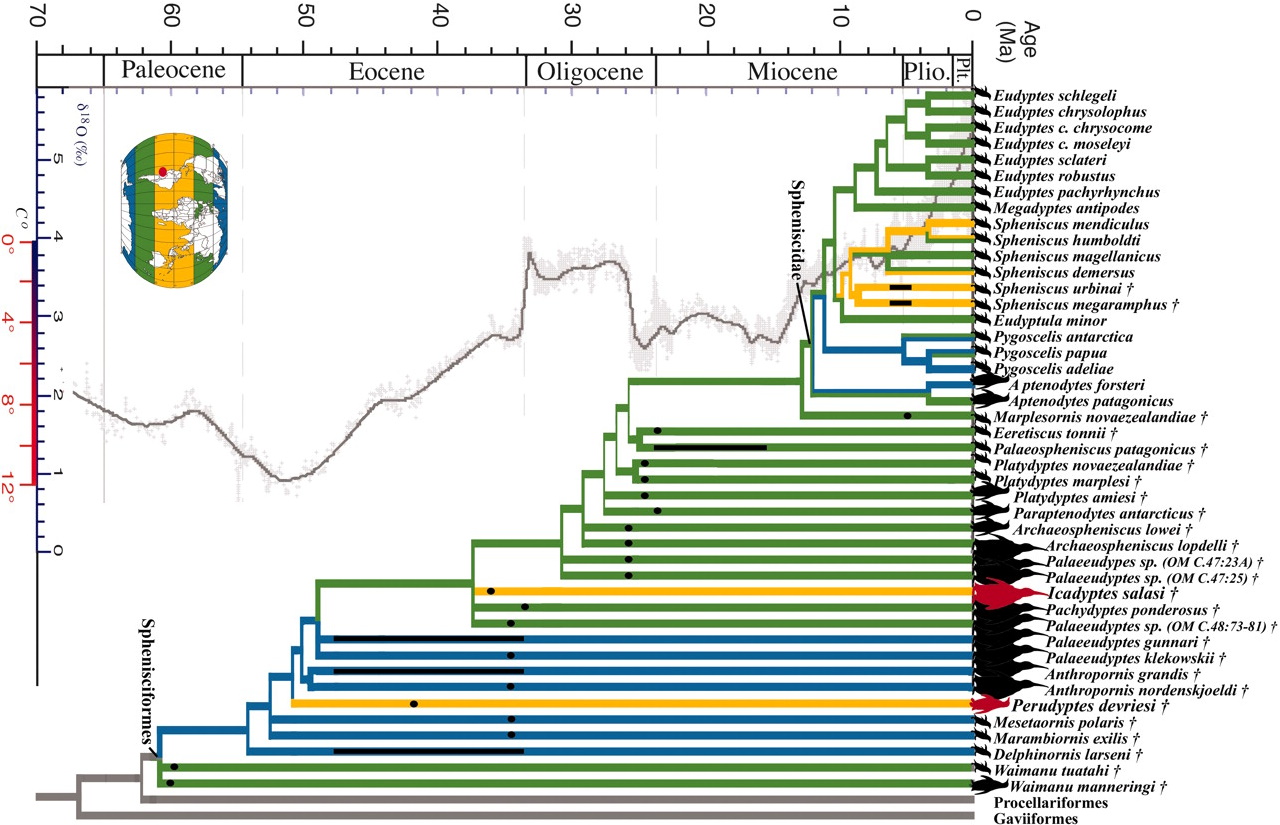
Cracraft and lead author Santiago Claramunt, a research associate in the Museum's Department of Ornithology, analyzed DNA sequences for most modern bird families with information from 130 fossil birds to generate a new evolutionary time tree.
"With very few exceptions, fossils of modern birds have been found only after the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction," said Claramunt. "This has led some researchers to suggest that modern birds didn't start to diversify until after this event, when major competitors were gone. But our new work, which agrees with previous DNA-based studies, suggests that birds began to radiate before this massive extinction."
After the K-Pg extinction, birds used two routes to cover the globe: first, to North America across a Paleogene Central American land bridge and then to the Old World; and second, to Australia and New Zealand across Antarctica, which was relatively warm at that time.
Claramunt and Cracraft also found that bird diversification rates increased during periods of global cooling.
"When the Earth cools and dries, fragmentation of tropical forests results in bird populations being isolated," Cracraft said. "Many times, these small populations will end up going extinct, but fragmentation also provides the opportunity for speciation to occur and for biotas to expand when environments get warm again. This work provides pervasive evidence that avian evolution has been influenced by plate tectonics and environmental change."
This work was supported by the Museum's F. M. Chapman Fund and the U.S. National Science Foundation, award #s 1241066 and 1146423.
Cracraft and lead author Santiago Claramunt, a research associate in the Museum's Department of Ornithology, analyzed DNA sequences for most modern bird families with information from 130 fossil birds to generate a new evolutionary time tree.
"With very few exceptions, fossils of modern birds have been found only after the Cretaceous-Paleogene (K-Pg) extinction," said Claramunt. "This has led some researchers to suggest that modern birds didn't start to diversify until after this event, when major competitors were gone. But our new work, which agrees with previous DNA-based studies, suggests that birds began to radiate before this massive extinction."
After the K-Pg extinction, birds used two routes to cover the globe: first, to North America across a Paleogene Central American land bridge and then to the Old World; and second, to Australia and New Zealand across Antarctica, which was relatively warm at that time.
Claramunt and Cracraft also found that bird diversification rates increased during periods of global cooling.
"When the Earth cools and dries, fragmentation of tropical forests results in bird populations being isolated," Cracraft said. "Many times, these small populations will end up going extinct, but fragmentation also provides the opportunity for speciation to occur and for biotas to expand when environments get warm again. This work provides pervasive evidence that avian evolution has been influenced by plate tectonics and environmental change."
This work was supported by the Museum's F. M. Chapman Fund and the U.S. National Science Foundation, award #s 1241066 and 1146423.
Story Source:
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by American Museum of Natural History. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
The above post is reprinted from materials provided by American Museum of Natural History. Note: Materials may be edited for content and length.
Journal Reference:
- S. Claramunt, J. Cracraft. A new time tree reveals Earth historys imprint on the evolution of modern birds. Science Advances, 2015; 1 (11): e1501005 DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1501005
American
Museum of Natural History. "Influence of Earth's history on the dawn of
modern birds: New time tree indicates that avian evolution was molded
by climate change and plate tectonics." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 11
December 2015.
<www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2015/12/151211145038.htm>.













No comments:
Post a Comment